1. What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a core branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on developing algorithms enabling computers to improve their performance through experience — in other words, to “learn” from data. Instead of being explicitly programmed step by step like traditional systems, machine learning allows systems to automatically identify patterns and make predictions or decisions based on the data they are given.
A simple and familiar example is an email spam filtering system. Rather than manually defining every keyword used to classify emails, a machine learning model analyzes and learns from thousands (or even millions) of sample emails to determine which messages are spam and which are important. Similarly, on advertising platforms, machine learning is widely applied to detect click fraud — fraudulent clicking behavior — helping advertisers optimize campaign performance and protect both business and client interests.
Machine learning is not just a technology — it is a new approach to problem-solving. It empowers systems to learn and adapt to previously unseen situations, something traditional rule-based programming simply cannot achieve.
2. How does machine learning work?
To understand how machine learning works, imagine teaching a child to distinguish between cats and dogs by showing them many images labeled “cat” or “dog.” Over time, the child learns to recognize features such as pointed ears, tails, or fur patterns without needing explicit instructions for every case. Machine learning operates in a similar way — but with data and algorithms instead of human intuition.
The basic machine learning workflow typically includes the following steps:
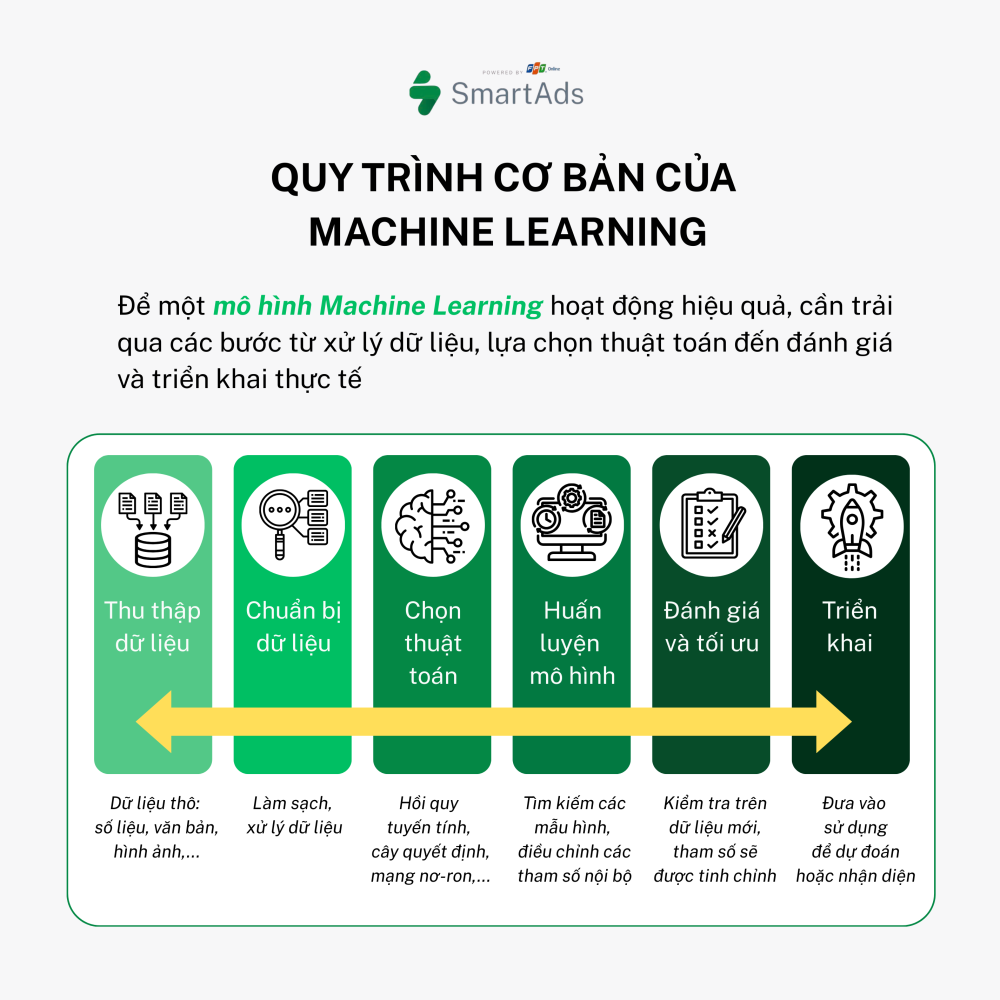
Step 1. Data Collection: Every machine learning model starts with data — the “raw material” for learning. This data can take many forms, including numerical values, text, images, or other formats.
Step 2. Data Preparation: Raw data is often messy, incomplete, or inconsistent. Data scientists clean, normalize, and preprocess the data to ensure it is suitable for training machine learning algorithms.
Step 3. Algorithm Selection: Depending on the task — prediction, classification, or data generation — an appropriate algorithm is selected, such as linear regression, decision trees, or neural networks.
Step 4. Model Training: This is the stage where the system “learns” from data. The algorithm searches for patterns and adjusts internal parameters to minimize prediction errors.
Step 5. Evaluation & Optimization: After training, the model is tested on new data to evaluate accuracy. If necessary, parameters are fine-tuned to improve performance.
Step 6. Deployment: Once the model performs well, it is deployed in real-world applications such as housing price prediction, facial recognition, or product recommendations on e-commerce platforms.
What makes machine learning especially powerful is that learning does not stop after deployment. A well-designed model can continue to improve as it receives new data — a process often associated with reinforcement learning or continuous model updates.
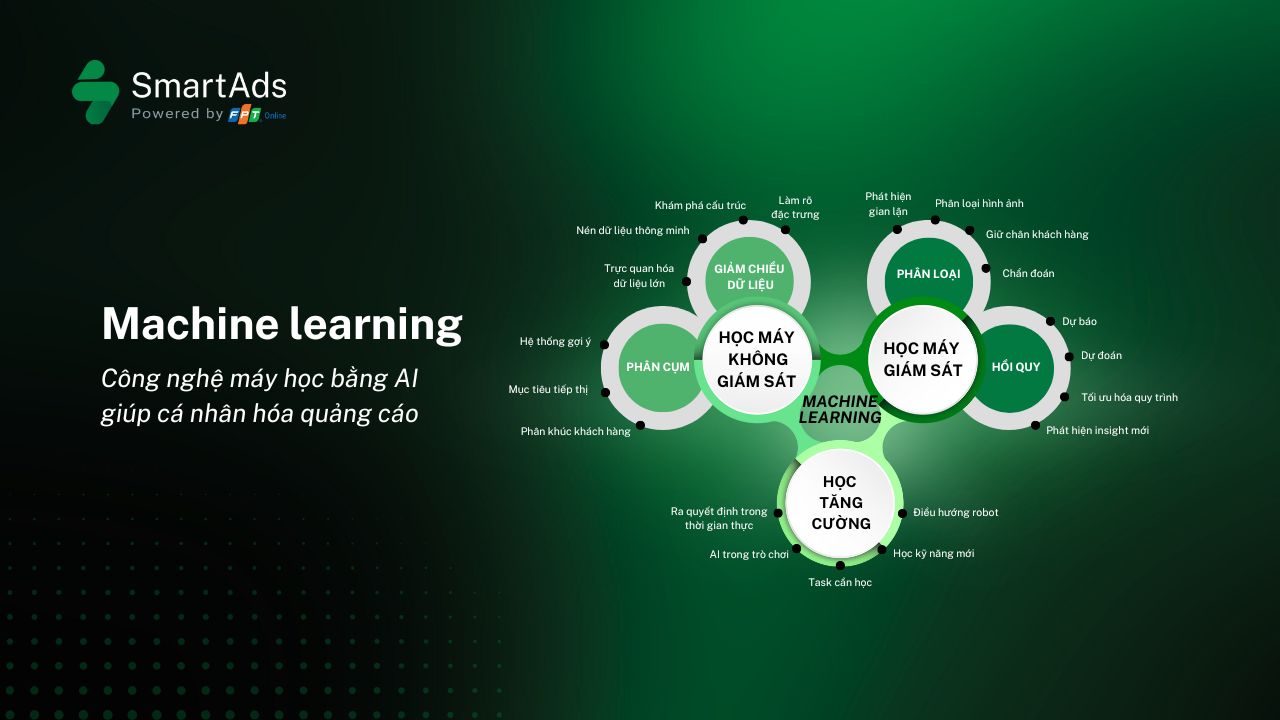
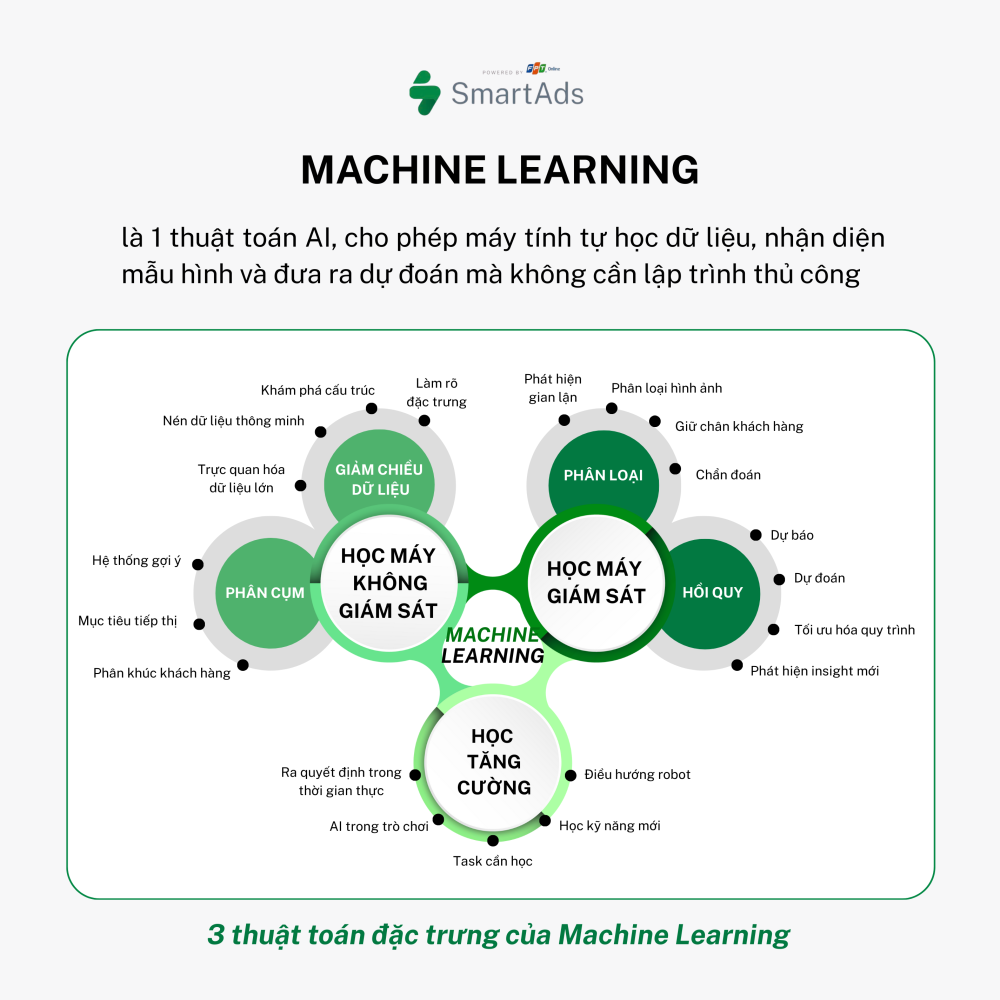
3. Common types of machine learning
a. Supervised Learning
This is the most widely used approach, where models are trained on labeled data — meaning each data sample is paired with a known outcome. For example, images of cats are labeled “cat,” and images of dogs are labeled “dog.” The model learns to predict labels for new, unseen data based on learned features.
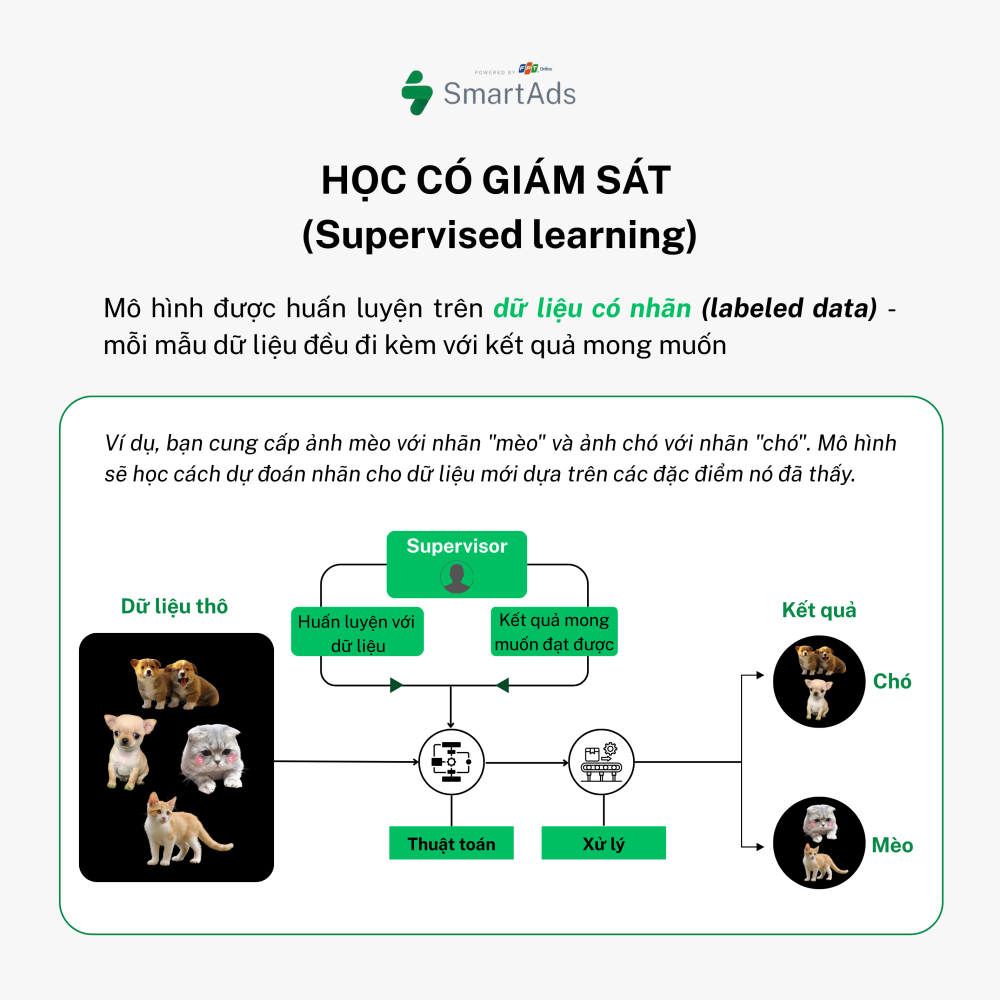
Applications: Housing price prediction, spam filtering, medical diagnosis based on symptoms.
Representative algorithms: Linear Regression, Support Vector Machines (SVM), Neural Networks.
b. Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning, data is unlabeled, and the model’s task is to discover hidden patterns or structures within the data. For example, when given images of different fruits without labels, the model can automatically group them based on shared features such as color or shape, without knowing their names in advance.
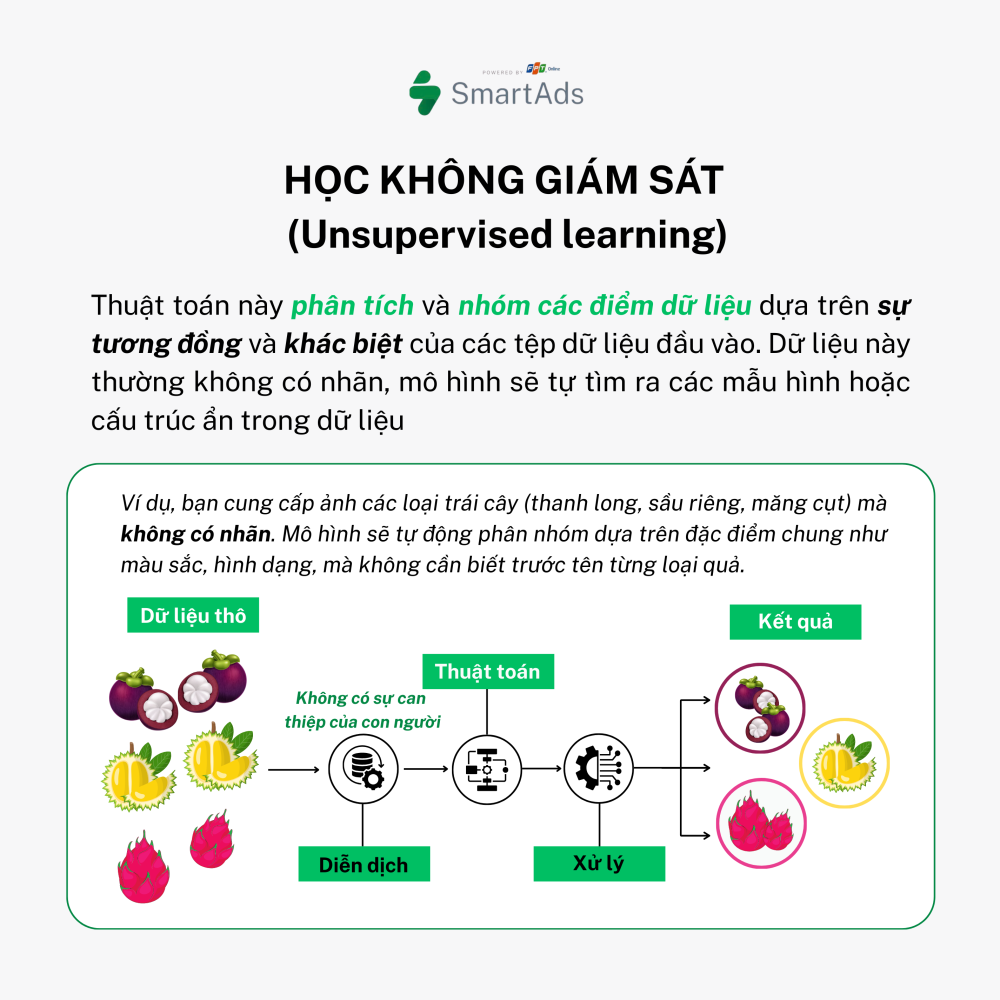
Applications: Market segmentation, data compression, anomaly detection.
Representative algorithms: K-Means Clustering, PCA (Principal Component Analysis).
c. Reinforcement Learning
This is a more advanced approach where models learn through trial and error within an environment to optimize a specific objective. Imagine a robot learning to walk: it experiments, falls, and continuously adjusts its actions to improve outcomes.
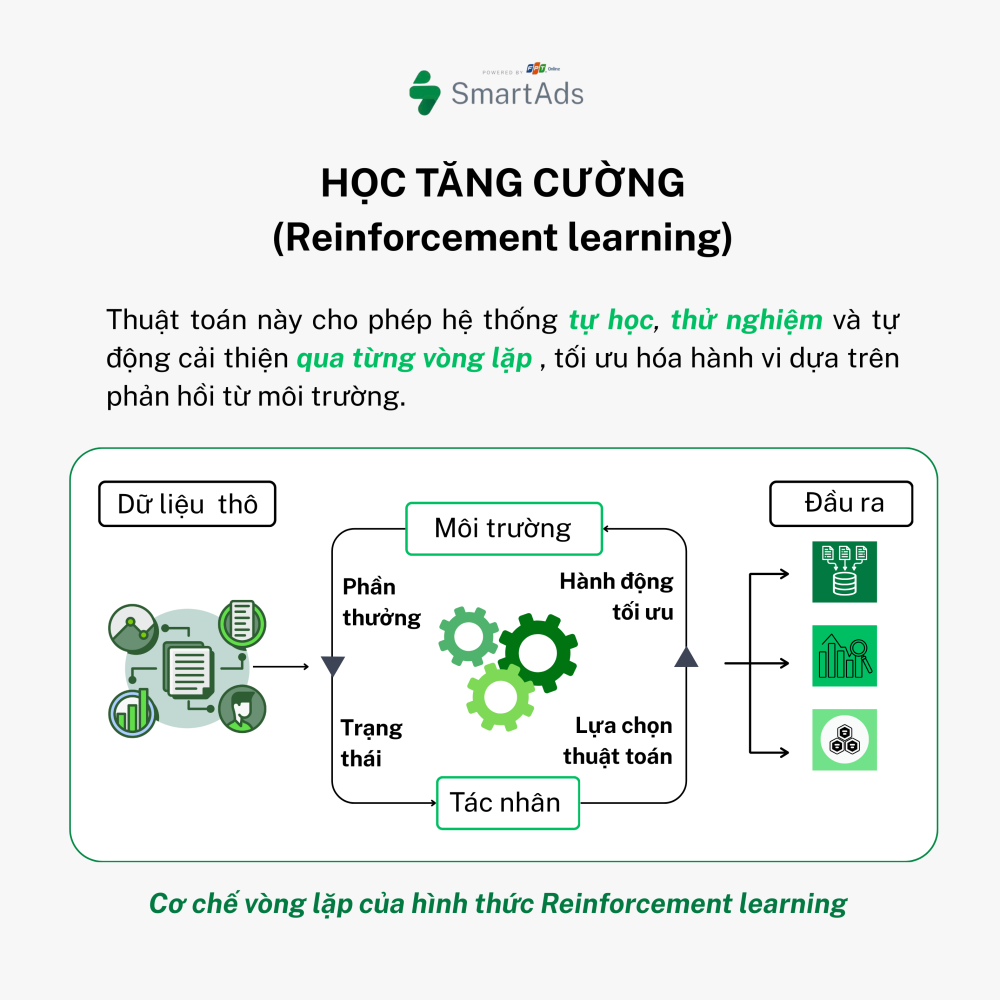
- Applications: Game playing (e.g., AlphaGo), robotics control, business strategy optimization.
- Representative algorithms: Q-Learning, Deep Reinforcement Learning.
4. Machine Learning Applications in Data Analysis
Machine learning enables highly efficient data analysis by automatically uncovering hidden patterns within massive datasets — a task that is extremely difficult to perform manually. In business, machine learning algorithms analyze customer behavior from purchase data, web browsing history, and social media interactions to predict consumer trends and deliver personalized experiences. In scientific fields, machine learning supports complex data analysis such as genomic sequencing or medical imaging, enabling earlier and more accurate disease detection. By continuously learning and adapting, machine learning not only accelerates analysis but also generates valuable insights that support better decision-making.
Given its vast potential, machine learning has been widely adopted in advertising, where data analysis plays a critical role. The typical implementation process includes the following steps:
Step 1: Data collection: impressions, clicks, CTR, browsing history, time on page, and more.
Step 2: Data preprocessing: cleaning, normalization, and data encoding.
Step 3: Model selection and training: Logistic Regression, Random Forest, XGBoost, etc.
Step 4: Deployment and monitoring: integrating the model into systems, tracking performance, and updating as needed.
Step 5: Analysis and decision-making: interpreting results and adjusting marketing strategies.
5. Machine Learning at SmartAds
Building on the processes above, SmartAds leverages machine learning to revolutionize the deployment of contextual advertising and personalized user experiences. By analyzing website and app content in real time, machine learning identifies the most relevant context for ad placement — without relying on cookies. Additionally, by harnessing large-scale behavioral data, SmartAds uses advanced data analysis and algorithms to accurately predict advertising performance. Key applications include:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR) Prediction: Machine learning predicts the likelihood that users will click on ads based on behavioral and demographic data. For example, if a user frequently searches for automotive content, SmartAds analyzes search history, ad placement, and browsing behavior to predict engagement with related ads.
- Customer Segmentation: SmartAds analyzes user data and automatically optimizes advertising strategies for different audience segments using clustering algorithms. High-value, medium-value, and low-value user groups are identified based on engagement metrics, enabling advertisers to prioritize the most effective targeting strategies.
- Ad Fraud Detection: Machine learning detects click fraud in real time through classification models and anomaly detection techniques. When abnormal clicking behavior is identified — such as unusually high click frequency from a single device or IP — fraudulent clicks are filtered out to protect advertising budgets.
- Ad Personalization: Collaborative Filtering and Deep Learning enable highly personalized advertising. For instance, when users read travel-related content, SmartAds algorithms instantly identify keywords such as “beach” or “hotel” and deliver relevant flight or vacation offers.
Machine learning is not merely a technical buzzword — it is a foundational force driving major breakthroughs in modern life, from Tesla’s self-driving vehicles to virtual assistants like Siri. Understanding its principles, workflows, and core types unlocks access to its vast potential. At SmartAds, machine learning is strategically applied to optimize advertising performance, detect fraud, and deliver measurable value for businesses in a data-driven digital ecosystem.