How Tracking Pixels Work?
A tracking pixel is generated by an ad platform or DSP and embedded into key pages of a website. When a user accesses the landing page or performs an action such as submitting a form, the pixel automatically fires and sends data back to the DSP. This allows the system to track user behavior throughout the journey and optimize campaign performance.
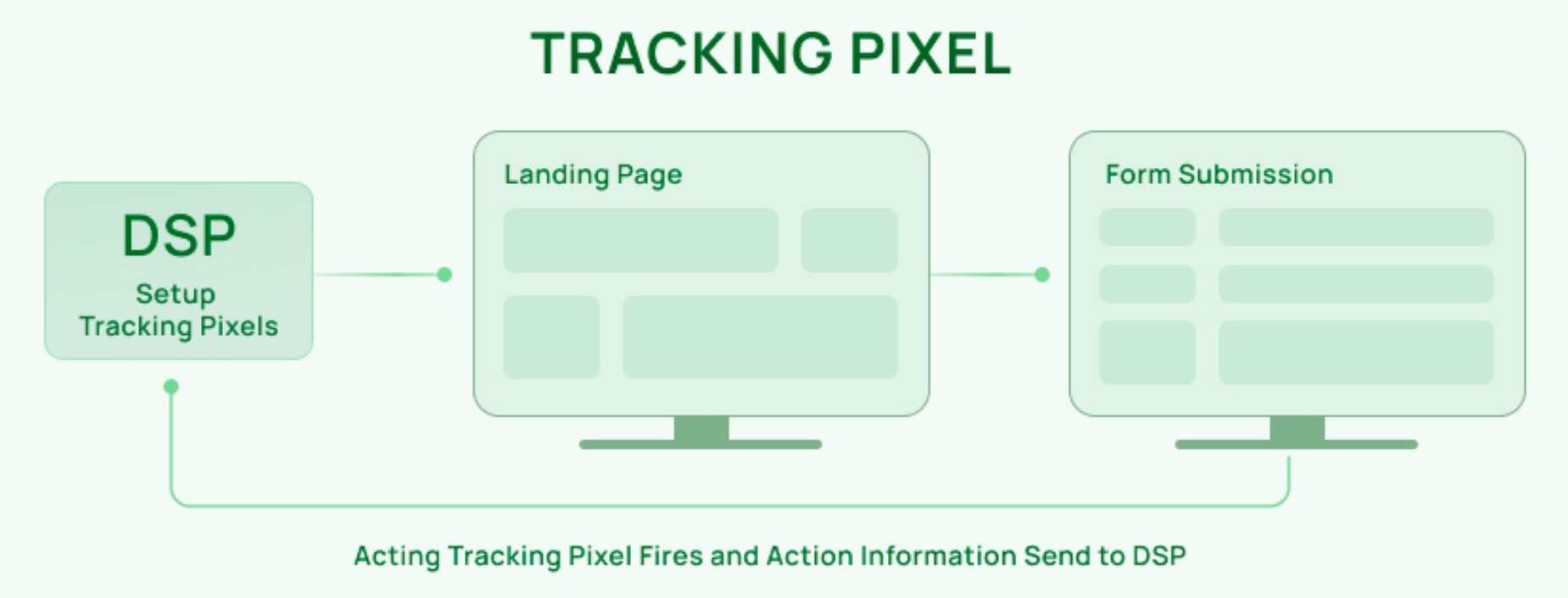
Based on the diagram, the workflow can be understood as follows:
-
The DSP generates and provides the tracking pixel code.
-
The pixel is placed on tracking points such as the landing page or the “Form Submission” page.
-
When a user visits or completes an action, the pixel fires and sends data back to the DSP for measurement and ad delivery optimization.
Below are the three technical steps explaining how a tracking pixel operates and how the database stores the data:
1. Adding the Tracking Pixel Code
To add a tracking pixel, you must embed its code into the webpage or email where you want to track user behavior. Depending on the platform, this code may be in HTML or JavaScript.
* Example of an HTML tracking pixel:
 img src="https://example.com/tracking-pixel.png" alt="" width="1" height="1" /
img src="https://example.com/tracking-pixel.png" alt="" width="1" height="1" /* Example of a JavaScript tracking pixel:
// JavaScript Tracking Pixel Code
(function() {
var pixel = new Image(1, 1);
pixel.src = "https://example.com/tracking-pixel.gif";
})();
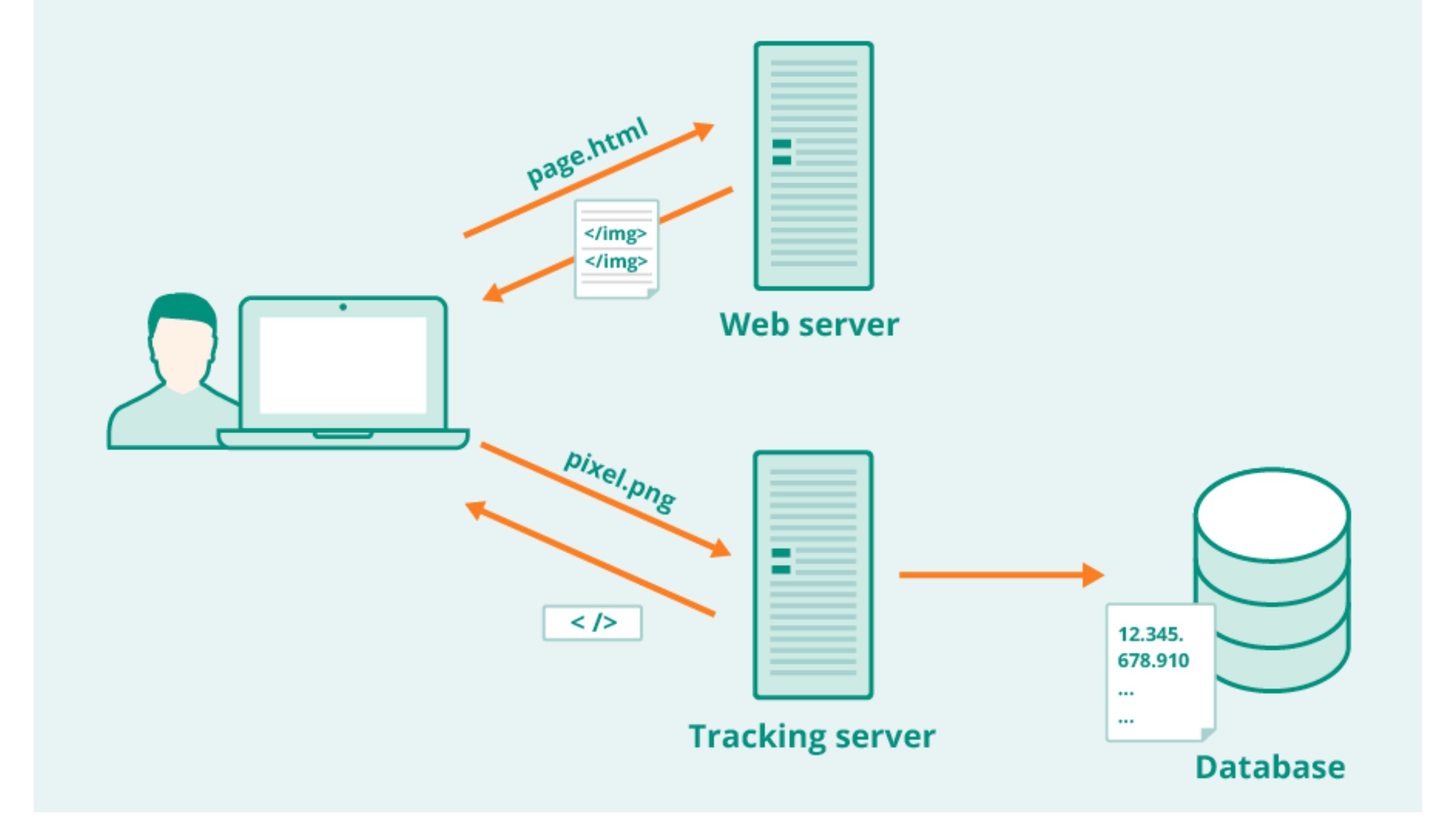
2. Pixel Stored on the Server
The pixel image is stored on a server, typically managed by the ad network or analytics platform. This server acts as a centralized repository of multiple pixels, and the pixel code functions as the “address” that the browser requests. When the pixel loads, the server receives a request to retrieve the tiny image file.
3. Pixel Loaded in the User’s Browser
When a user opens a webpage, email, or ad containing the tracking pixel, their browser automatically requests all assets—including the pixel. During this request, the browser also sends information back to the server, such as IP address, browser type, screen resolution, and more.
What Data Do Tracking Pixels Collect?
The primary function of a pixel is to record user behavior and interactions. Depending on configuration, a pixel may collect:
-
IP address
-
Timestamp of the visit or action
-
Device and browser type
-
Referrer URL
-
Pageviews
-
On-page engagement
-
Cookies
-
Screen resolution
-
Conversion data
-
Email interactions (opens, link clicks)
This data serves as a foundation for ad optimization, user behavior analysis, and accurate conversion funnel measurement.
Common Types of Tracking Pixels
Below are the most commonly used tracking pixels in digital marketing:
1. Conversion Pixel
Used to track key actions on a website, such as:
-
Form submissions
-
Newsletter sign-ups
-
Purchases
-
File downloads
The pixel fires only when the desired action is completed, helping businesses measure campaign conversion performance accurately.
2. Retargeting Pixel
Used to record user behavior on the website, such as:
-
Pages visited
-
Time spent on page
-
Scroll depth
-
Visit frequency
This data is used to build custom audiences for remarketing campaigns.
3. Analytics Pixel
Used to analyze website performance and collect metrics like pageviews, session duration, demographics, user journeys, and interactions. Tools like Google Analytics rely on this type of pixel to build detailed reports and real-time dashboards.
4. Social Media Pixel
Platforms such as Facebook, TikTok, and X (Twitter) provide their own pixels for advertisers. These pixels track post-ad behaviors to measure conversions and optimize campaigns.
5. Email Tracking Pixel
Email tracking pixels measure open rates, click-through rates, engagement levels, and unsubscribe behavior. This helps marketers optimize subject lines, content, and CTAs.
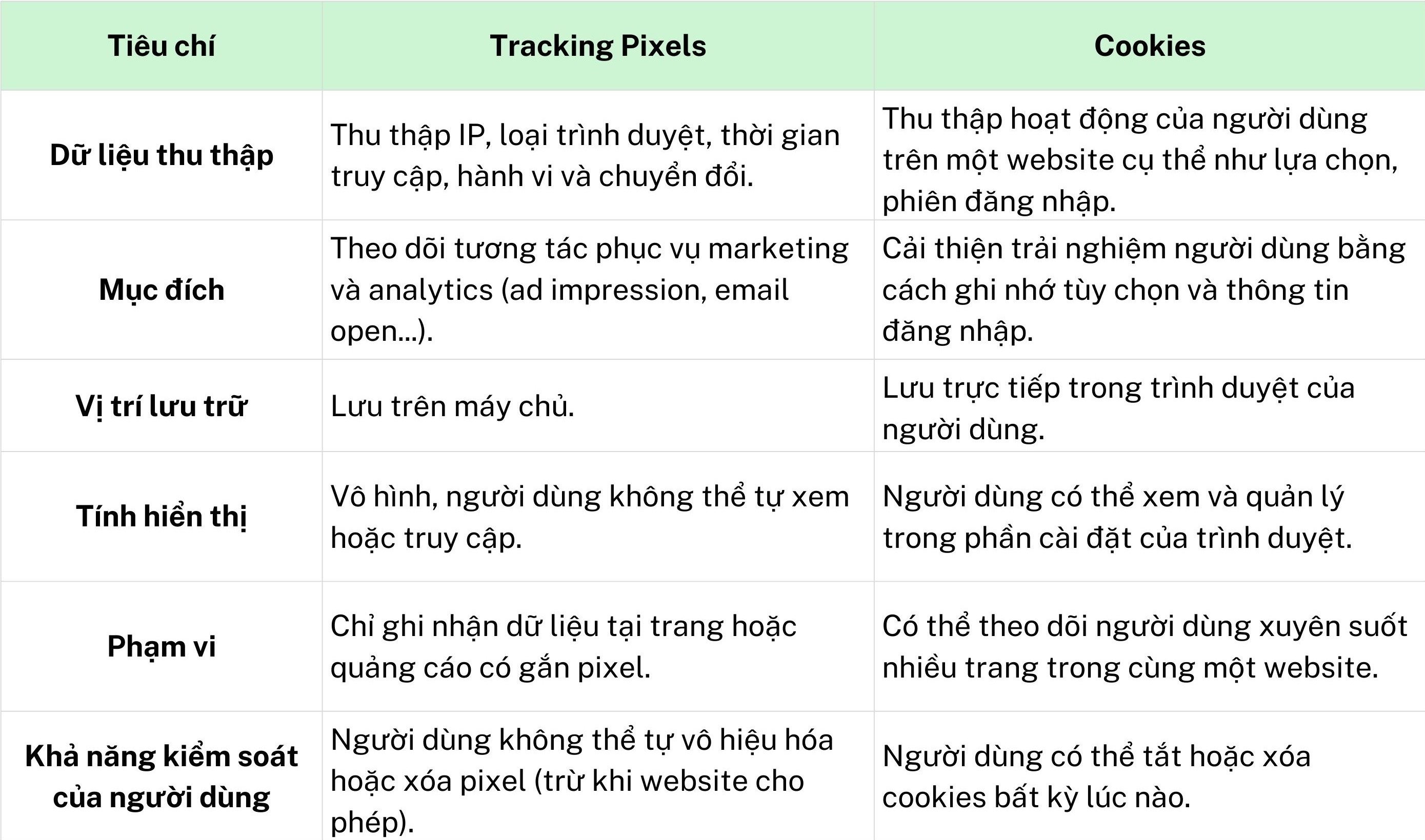
The Difference Between Tracking Pixels and Cookies
Many people often confuse tracking pixels with cookies because both collect user data. However, they operate in completely different ways and serve different purposes in digital marketing.
Cookies are small text files stored directly on a user's browser. They remember session information and personal preferences (such as language, login status, or on-site behavior). Thanks to cookies, marketers can personalize the user experience and understand individuals’ browsing history.
Tracking pixels, on the other hand, are tiny, invisible image files stored on a server. When a user loads a page, opens an email, or sees an ad containing a pixel, the image is downloaded and sends data back to the server. Pixels capture behaviors such as page views, email opens, ad impressions, conversions, etc. Notably, tracking pixels can also request access to cookies already stored in the browser.
Below is a visual comparison between tracking pixels and cookies:
>>> Learn more about SmartAds retargeting ads here.
Applications of Tracking Pixels in Marketing
Below are the most common ways businesses can leverage tracking pixels to improve marketing performance:
1. Website Analytics and Conversion Tracking
By implementing pixels on your website, you can track:
- User navigation paths
- The time spent on each page
- How users move between pages
- Pages or content that drive conversions (sign-ups, downloads, purchases, etc.)
This data helps optimize content, improve user experience, and increase conversion rates.
2. Personalizing User Experience
Tracking pixels provide deeper insights into user preferences and behavior. This information allows you to create tailored web experiences based on their previous interactions. This can include personalized content, targeted ads, promotional programs, and more.
3. Boosting Engagement and CTR
If your goal is to increase engagement and click-through rates (CTR), tracking pixels are essential. They reveal which content performs best, which pages/products attract the most attention, which emails have the highest open/click rates, and which CTAs are most effective. From there, you can optimize your content strategy to improve engagement.
4. Optimizing Advertising Performance
Tracking pixels help measure which ads generate impressions, which ads receive the most clicks, and which ads drive conversions. This enables marketers to calculate ROI, allocate budgets efficiently, and maximize campaign performance.
5. Retargeting
One of the most powerful uses of tracking pixels is retargeting. Pixels identify users who visited your website but didn’t complete a purchase, those who viewed products without taking further action, or those who abandoned the funnel mid-way. Using this data, you can run highly accurate retargeting campaigns to increase return visits and conversions.
Popular Platforms Offering Pixel Tracking
Pixel tracking is increasingly adopted to improve advertising efficiency and optimize user journeys. Below are widely used platforms offering pixel solutions:
-
LinkedIn Pixel / Insight Tag: Supports conversion tracking and精准 targeting for 500M+ professionals based on job title, industry, or role. LinkedIn also allows targeting across multiple decision-making stages.
-
Google Analytics Tracking Code: By adding tracking code to your site, businesses can easily collect critical behavioral data to make informed business and marketing decisions.
-
Facebook Pixel: Tracks website traffic, measures conversions, optimizes ad spend, and creates custom audiences for highly effective retargeting.
-
Google Ads Conversion Tracking: Measures ad click quality and conversion value, while expanding reach to new customers through custom audiences.
-
Google Tag Manager (GTM): A tag management system used to deploy and update tracking tags without modifying source code.
-
Twitter Pixel: Tracks user behavior after interacting with ads, capturing actions such as clicks, retweets, likes, impressions, and attributes conversion data to Twitter’s analytics system.
- SmartAds Pixel: Designed to help brands accurately track user behavior after interacting with ads across the news ecosystem. The pixel captures views, engagements, conversions, and enables marketers to build highly accurate remarketing audiences. With real-time data and easy website integration, SmartAds Pixel is a key tool for evaluating performance, optimizing budget, and maximizing overall digital campaign efficiency.
>>> Learn how to create UTM tracking and set up SmartAds pixel here.
Privacy Considerations When Using Tracking Pixels

A few years ago, tracking pixels were considered a “must-have” tool. Today, users are more concerned about privacy, and regulators have tightened compliance requirements. The biggest challenge is that pixels collect data invisibly, raising concerns about transparency. Many users are unaware they are being tracked when browsing a website or viewing an ad.
Additionally, regulations like GDPR (Europe) and CPRA (California) require businesses to clearly disclose what data is collected and explain its purpose when requesting user consent.
So, How Do You Use Tracking Pixels While Remaining Privacy-Compliant?
Below are essential steps to ensure your pixel implementation is transparent and compliant with privacy regulations.
1. Obtain User Consent
- Clear notification: Display a banner or pop-up informing users that the website uses tracking pixels.
- Use a Consent Management Platform (CMP): Implement a CMP to collect and manage user choices, allowing them to accept – decline – customize tracking levels.
- Set consent requirements: Depending on your policy, you may require explicit consent or allow access without mandatory consent.
2. Limit and Anonymize Data
- Collect for defined purposes: Only gather data necessary for marketing activities.
- Anonymize data: Avoid storing personally identifiable raw data; convert data into anonymized formats to reduce security risks.
- Manage Pixel IDs properly: For tools like Meta Pixel, ensure safe ID management and follow platform guidelines.
3. Provide Opt-out & Data Control Mechanisms
- Flexible opt-in/opt-out: Even after consenting, users should be able to disable tracking anytime.
- Data retention policy: Maintain clear rules on how long data is stored and keep it only for necessary periods.
- Transparent privacy policy: Publish an easy-to-understand Privacy Policy outlining data types, purposes, and protection measures.
4. Pixel Setup and Configuration
- Install the pixel: Follow implementation instructions from your platform (SmartAds, Meta Business Manager, HubSpot, Google Tag Manager, etc.).
- Configure tracking events: When installing a pixel, define which events to track (e.g., ViewContent, AddToCart, Lead, Purchase) and place event codes in the correct locations.
Conclusion
In summary, tracking pixels play a crucial role in measuring and optimizing campaign performance—from tracking user interactions to identifying conversions. By implementing pixels correctly and complying with privacy regulations, brands can fully leverage them as a powerful tool to understand user behavior and enhance digital marketing effectiveness.