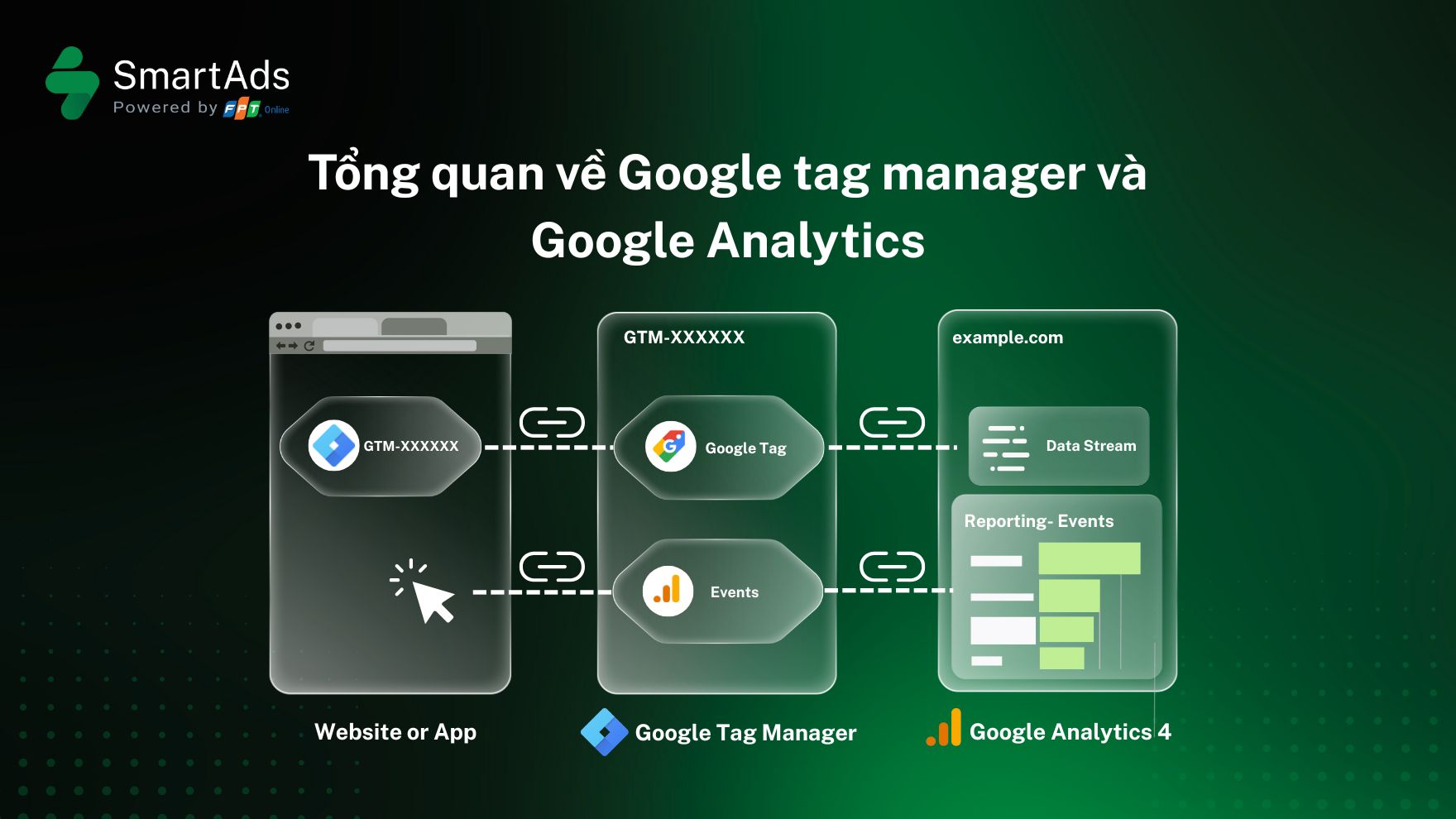
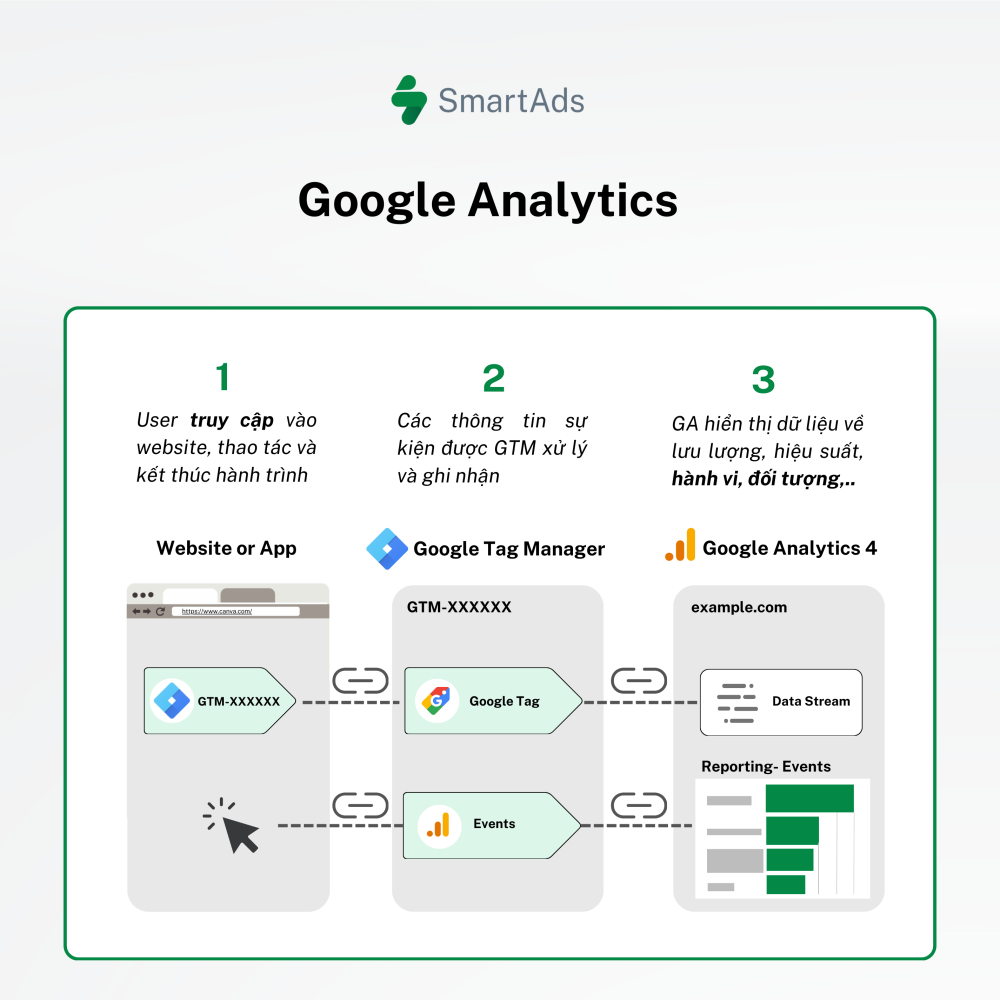
I. Google Analytics and its role in user behavior analysis
Google Analytics is a platform developed by Google that enables you to track and analyze website traffic. From the number of users and time spent on site to specific actions such as button clicks, purchases, or form submissions, Google Analytics provides a comprehensive view of how users interact with your website.
Beyond raw data, Google Analytics helps you deeply understand user behavior through event-based tracking, allowing data-driven decisions to improve and optimize website performance. This makes Google Analytics an essential tool for marketers, business owners, and SEO specialists alike.
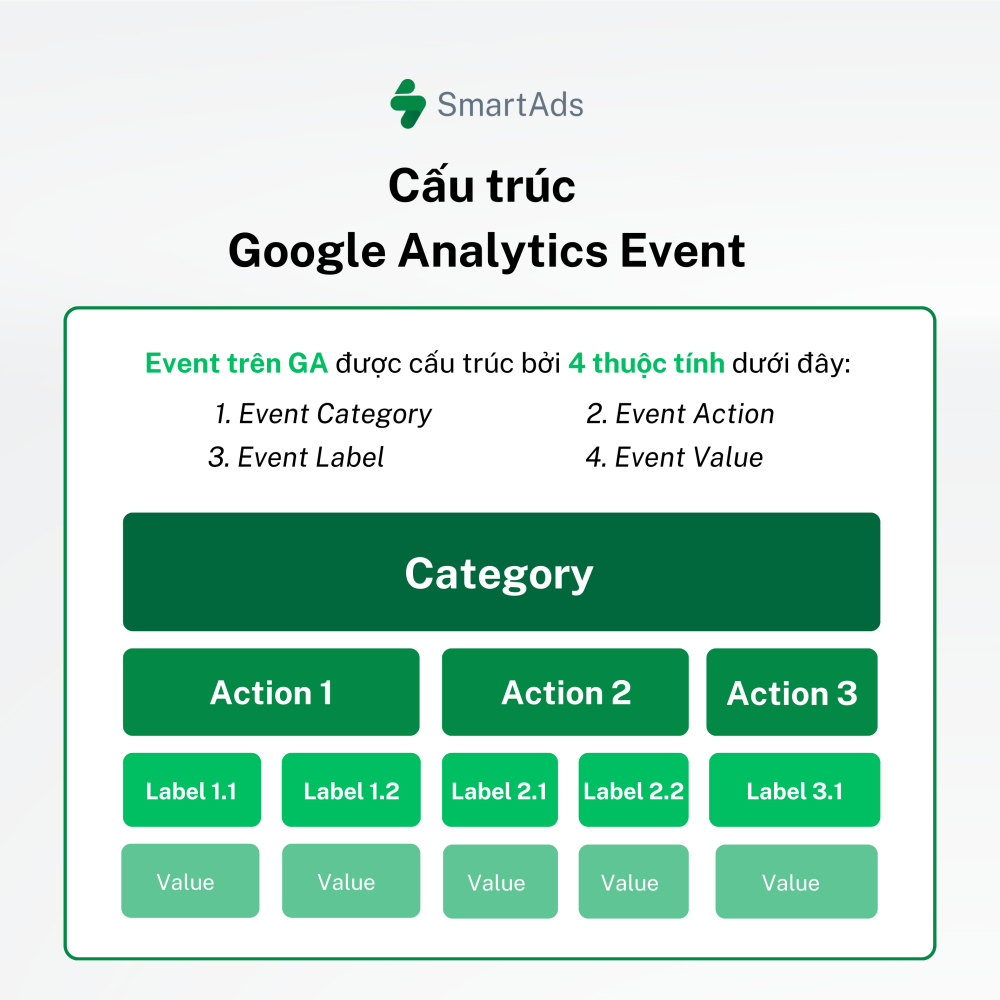
II. Event classification in Google Analytics
In Google Analytics, Events represent specific actions that users take on your website. These events are typically structured into four main components:
1. Category:
Event Category is a key attribute used to group related events together. It helps organize and analyze user interactions on a website or app more effectively by allowing comparisons across different event groups.
Example: You can define “Video” as an Event Category to group all video-related interactions such as “play,” “pause,” or “fullscreen.”
2. Action:
Event Action describes the specific interaction a user performs on the website or app. It differentiates types of interactions within the same Event Category and provides more granular insight into user behavior.
Example: Following the example above, “play,” “pause,” and “fullscreen” are individual Event Actions within the “Video” category.
3. Label:
Event Label is an optional attribute in Google Analytics that adds additional context to an event. It is commonly used to describe the specific content or element that users interacted with.
Example: Within the “Video” category, the “Play” action may include labels such as “Play Video A,” “Play Video B,” or “Play Video C.”
4. Value:
Event Value is an optional numeric attribute assigned to an event. This value can represent time, monetary value, scores, or any quantitative metric that is meaningful for data analysis and business evaluation.
Example: The label “Play Video A” is triggered 30 times, with an average watch time of 60 seconds.
III. How to define events to track
To maximize the effectiveness of Event Tracking, it is essential to identify the most important events on your website. Below are several steps to guide this process:
1. Define business objectives: Start by clearly identifying your core business goals.
For example: increasing sales revenue, improving conversion rates, growing newsletter subscriptions, or boosting content downloads.
2. List key user actions: Based on your objectives, identify the user interactions you want to track. These actions should reflect meaningful engagement with your website. Common events include:
- Clicking links
- Downloading content
- Adding products to cart
- Completing purchases
- Subscribing to newsletters
However, it is important to note that implementing too many Event Tracking tags can slow down website performance, introduce data noise, exceed Google Analytics tracking limits, and increase operational costs. This negatively impacts user experience and complicates data analysis. Therefore, businesses should focus on tracking only high-impact events aligned with their defined objectives.
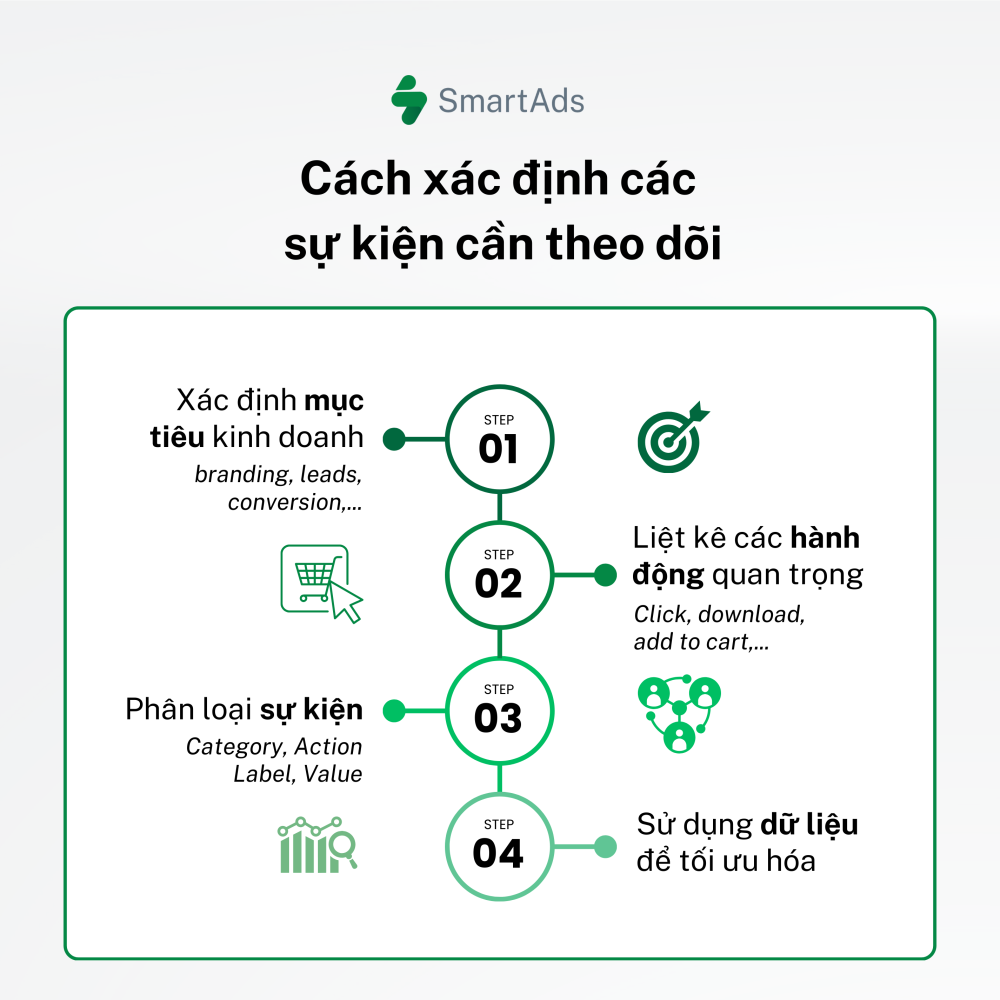
3. Classify events: Group events by shared categories, detailed actions, contextual labels, and measurable values. For example:
- Event Category: "Ebook"
- Event Action: "Download", "Preview"
- Event Label: "Download Ebook A", "Download Ebook B", "Preview Ebook A"
- Event Value: "0"
4. Use data to optimize:
Analyze event data to gain deeper insights into user behavior and identify areas for improvement. At the same time, continuously monitor and evaluate whether tracked events remain aligned with evolving business objectives.
Example: If the “Add to Cart” event for Product A shows high engagement but low purchase completion, this may indicate friction in the checkout process or other factors influencing purchase decisions.
IV. How server-side tagging (SST) works in Google Tag Manager
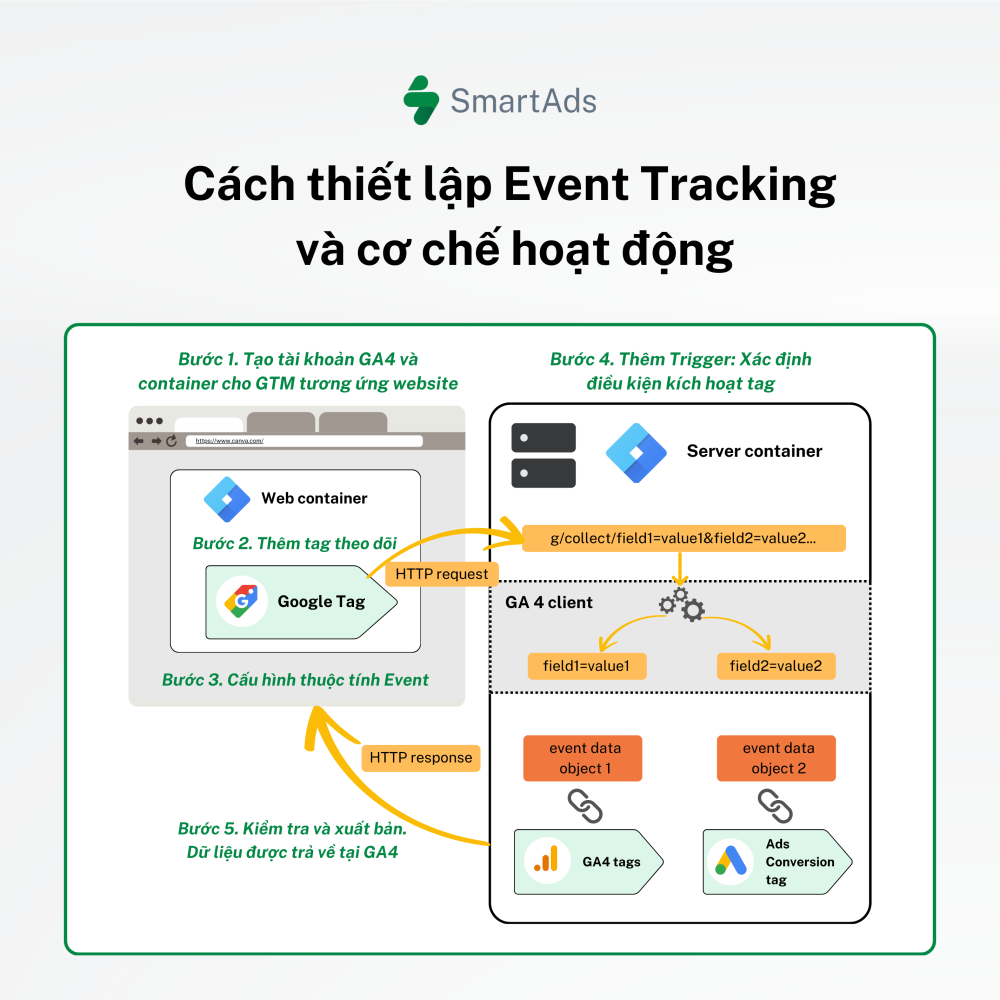
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a tool that allows you to manage and deploy tracking codes on your website without directly modifying the site’s source code.
- The Web container (client-side browser) contains Google Tags that run in the user’s browser. When an event occurs, the tag sends an HTTP request with data (e.g., field1=value1&field2=value2) to the Server container.
- The Server container receives data from the Web container via HTTP requests.
- The GA4 client within the Server container parses incoming requests and separates them into individual event data objects.
- The Server container forwards data to GA4 tags (Google Analytics 4) and Ads Conversion tags (Google Ads).
- Finally, the Server container can return an HTTP response to the browser if additional measurement is required.
>>> Step-by-step guide to setting up UTM tracking and SmartAds Pixel.

V. Google Tag Manager usage guide
Below are the steps to set up Event Tracking using Google Tag Manager:
Step 1. Create a GA4 account and set up a corresponding GTM container for the website you want to track.
Step 2. Add tracking tags: Create a new tag and select “Google Analytics: GA4 Event” as the tag type.
Step 3. Configure event parameters: Enter event details such as Category, Action, Label, and Value.
Step 4. Add triggers: Define trigger conditions, for example when a user clicks a specific button.
Step 5. Test and publish: Use Preview mode to validate tracking before publishing the container.
Conclusion
Google Analytics and Event Tracking are powerful tools for understanding user behavior and optimizing website performance. By classifying events, identifying what to track, and implementing Event Tracking through Google Tag Manager, businesses can transform data into actionable insights and achieve their marketing objectives.
Currently, SmartAds provides a premium digital advertising platform across major online publishers, helping brands reach the right audiences and drive high-quality traffic to their websites. To achieve holistic optimization, combining SmartAds advertising campaigns with user behavior measurement through Google Analytics is essential for brands focused on conversion tracking. This integration not only ensures accurate performance measurement but also delivers valuable data to support strategic marketing decisions.