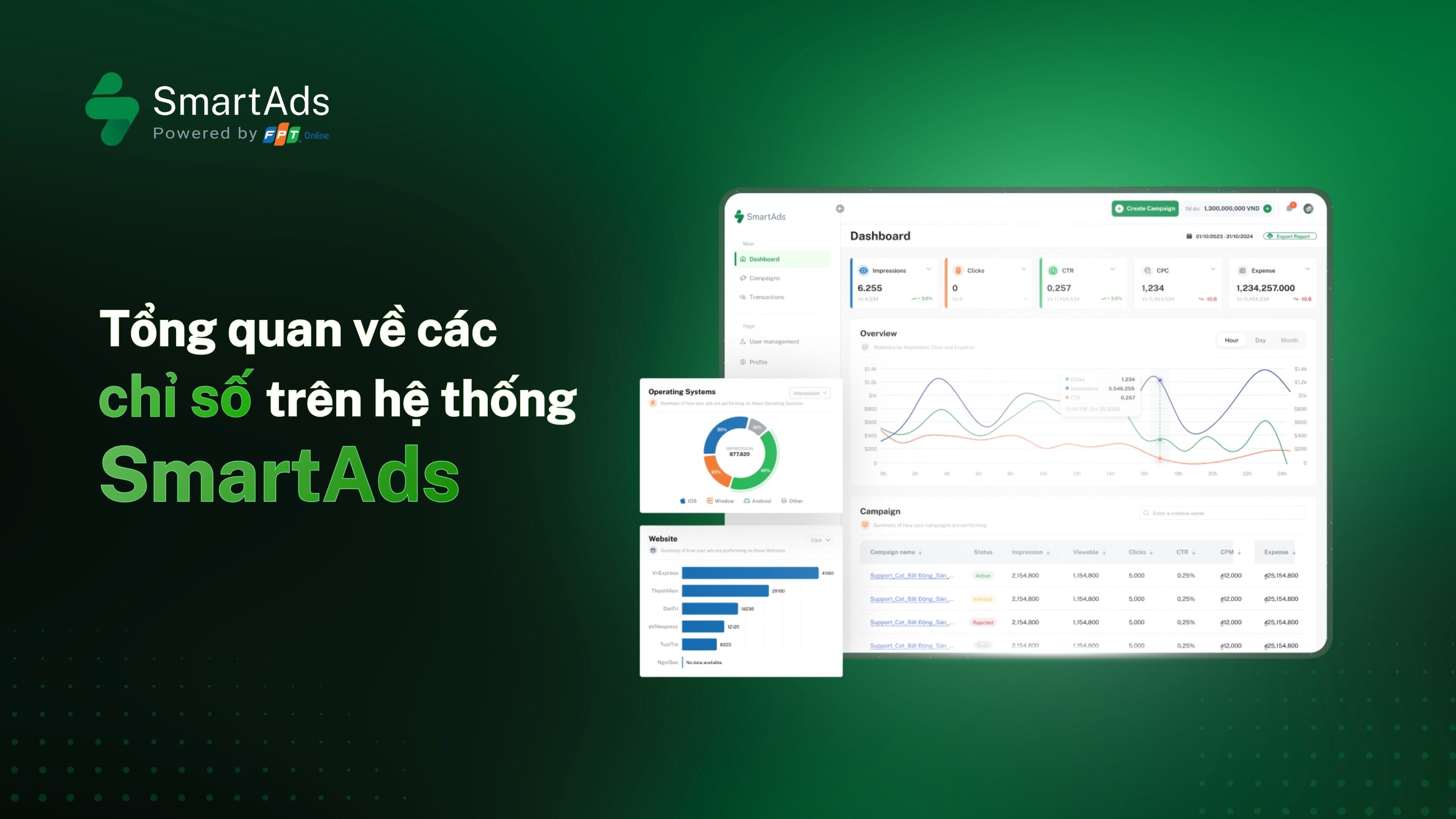
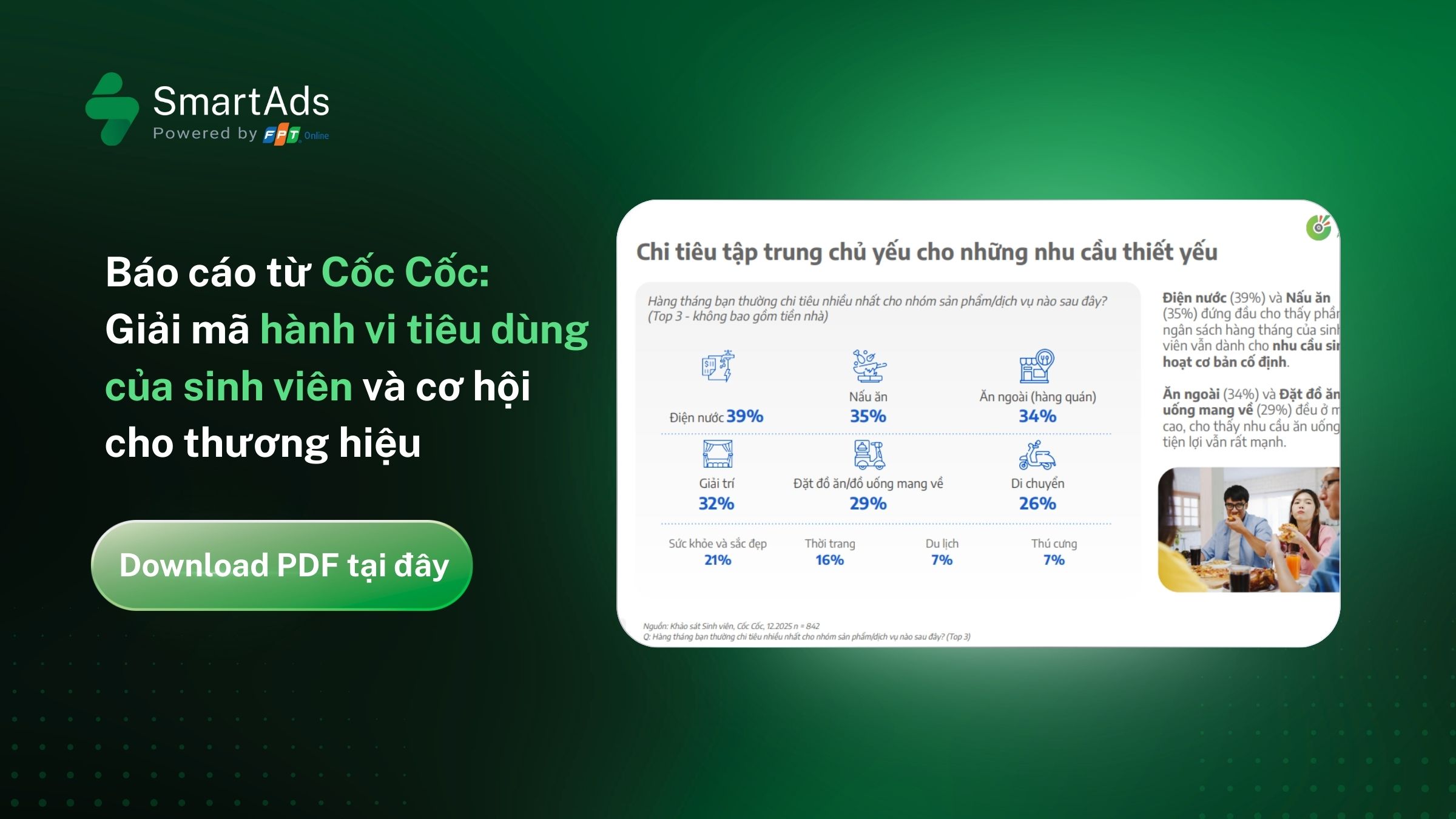
I. Lead là gì?
Lead, hay còn gọi là khách hàng tiềm năng, là những người đã thể hiện sự quan tâm đến sản phẩm hoặc dịch vụ của doanh nghiệp theo một cách nhất định. Sự quan tâm này có thể được thể hiện qua nhiều hành động cụ thể, chẳng hạn như để lại thông tin liên hệ trên biểu mẫu đăng ký website, nhắn tin trực tiếp qua Fanpage hoặc tương tác với các nội dung quảng cáo. Khi một người thực hiện những hành động này, họ được ghi nhận là Lead vì họ đã chủ động tiếp cận doanh nghiệp thay vì bị động nhận thông tin từ các kênh quảng cáo đại trà. Chính vì vậy, quá trình này được đánh giá là xuất phát từ nhu cầu thực tế của khách hàng, khác với những phương thức tiếp cận ngẫu nhiên như telesales hay email spam. Ngoài yếu tố chủ động, Lead còn được phân loại dựa trên cách họ trở thành khách hàng tiềm năng và vị trí của họ trong hành trình mua hàng. Dựa trên các tiêu chí này, Lead thường được chia thành bốn nhóm chính trong toàn bộ quá trình Lead generation, giúp doanh nghiệp xây dựng chiến lược tiếp cận phù hợp với từng giai đoạn.

1. Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL)
MQL là nhóm khách hàng tiềm năng được bộ phận Marketing đánh giá dựa trên mức độ tương tác của họ với thương hiệu.
Ví dụ: một khách hàng có thể được coi là MQL nếu họ đã thực hiện các hành động như tải tài liệu eBook, đăng ký hội thảo web (webinar), thường xuyên mở email tiếp thị, hoặc dành nhiều thời gian trên trang sản phẩm mà không thoát ngay. Những hành động này cho thấy họ quan tâm đến sản phẩm/dịch vụ, nhưng chưa sẵn sàng để mua ngay. Mỗi doanh nghiệp có tiêu chí riêng để xác định một người lạ có đủ điều kiện trở thành MQL. Sau khi xác định danh sách MQL, bộ phận Marketing sẽ chuyển họ cho bộ phận Sales để tiếp tục quá trình chuyển đổi.
2. Sales Qualified Lead (SQL)
SQL là nhóm khách hàng tiềm năng có khả năng cao để chuyển đổi thành khách hàng thực sự. Họ đã vượt qua các tiêu chí đánh giá từ Marketing hoặc Sales và thể hiện rõ nhu cầu mua hàng.
Ví dụ: Một khách hàng truy cập website của một công ty bất động sản sau khi thấy quảng cáo về các dự án căn hộ cao cấp. Khách điền form để nhận bảng giá và thông tin chi tiết về dự án. Bộ phận marketing xác định đây là một Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL). Khi nhân viên sales liên hệ, khách hàng cho biết đang tìm mua một căn hộ 2 phòng ngủ để ở, có ngân sách khoảng 3 tỷ đồng và dự định mua trong vòng 3 tháng. Họ quan tâm đến tiến độ thanh toán, chính sách vay ngân hàng và muốn tham quan thực tế căn hộ mẫu. Sau khi xác minh nhu cầu thực sự và khả năng tài chính của khách hàng, sales đánh giá đây là một Sales Qualified Lead (SQL) và tiếp tục dẫn dắt qua quá trình tư vấn, tham quan và chốt giao dịch.
3. Product Qualified Lead (PQL)
PQL là khách hàng đã trải nghiệm sản phẩm và có dấu hiệu sẵn sàng nâng cấp lên phiên bản trả phí. Nhóm này phổ biến ở các doanh nghiệp cung cấp bản dùng thử hoặc phiên bản miễn phí giới hạn. Nhờ các tùy chọn nâng cấp trong sản phẩm, doanh nghiệp có thể chuyển đổi PQL thành khách hàng trả phí.
Ví dụ: Một người dùng đăng ký tài khoản miễn phí trên Spotify để nghe nhạc nhưng bị giới hạn bởi các quảng cáo, không thể chọn bài hát theo ý muốn (chỉ có thể nghe theo chế độ shuffle) và bị giới hạn số lần bỏ qua bài hát. Sau một thời gian sử dụng, người này bắt đầu cảm thấy bất tiện khi bị gián đoạn bởi quảng cáo và muốn có trải nghiệm tốt hơn. Đặc biệt, khi Spotify gửi thông báo đề xuất nâng cấp lên Spotify Premium với ưu đãi dùng thử 3 tháng miễn phí, họ cân nhắc và quyết định đăng ký gói trả phí để có trải nghiệm tốt hơn. Đây chính là một ví dụ điển hình về PQL (Product Qualified Lead), khi người dùng đã trải nghiệm sản phẩm và bắt đầu nhận ra giá trị từ việc nâng cấp lên gói trả phí để có trải nghiệm tốt hơn.
4. Service Qualified Lead
Đây là nhóm khách hàng đã chủ động bày tỏ mong muốn nâng cấp dịch vụ hoặc mua thêm sản phẩm. Nhóm khách hàng này khác với MQL – những người mới chỉ thể hiện sự quan tâm thông qua các hoạt động tiếp thị, và PQL – những người đã trải nghiệm sản phẩm và có dấu hiệu muốn nâng cấp, Service Qualified Lead là những người trực tiếp yêu cầu thay đổi gói dịch vụ hoặc mua thêm.
Ví dụ, khi một khách hàng liên hệ với bộ phận chăm sóc khách hàng để yêu cầu nâng cấp gói đăng ký, nhân viên dịch vụ sẽ xác nhận nhu cầu và chuyển họ sang nhóm Service Qualified Lead để đội ngũ Sales tiếp tục quy trình bán hàng. Service Qualified Lead thường có ý định mua rõ ràng nhất, giúp quá trình chuyển đổi diễn ra nhanh chóng hơn.
II. Lead Generation là gì?
Lead Generation là quá trình thu hút và chuyển đổi người lạ thành khách hàng tiềm năng bằng cách khiến họ thể hiện sự quan tâm đến sản phẩm hoặc dịch vụ của doanh nghiệp. Một số công cụ phổ biến để tạo Lead bao gồm bài viết blog, tài liệu hướng dẫn, sự kiện trực tiếp, phiếu giảm giá,… Để một người lạ trở thành khách hàng tiềm năng, họ thường trải qua một quy trình gồm nhiều bước, từ việc nhận thức về thương hiệu, quan tâm đến nội dung hoặc ưu đãi, cho đến hành động đăng ký hoặc cung cấp thông tin liên hệ. Sau đây là các bước cụ thể trong quy trình chuyển đổi người lạ thành khách hàng tiềm năng.

1. Quy trình tạo Lead (Lead Generation Process)
Bước 1: Khám phá doanh nghiệp
Người truy cập tìm thấy doanh nghiệp của bạn thông qua các kênh marketing như website, blog hoặc mạng xã hội.
Bước 2: Nhấp vào CTA (Call to Action)
Họ tương tác với một lời kêu gọi hành động (CTA), có thể là một nút bấm, hình ảnh hoặc thông điệp mời họ thực hiện một thao tác cụ thể.
Bước 3: Truy cập trang đích (Landing Page)
CTA dẫn người dùng đến trang đích – nơi được thiết kế để thu thập thông tin khách hàng tiềm năng thông qua một đề nghị giá trị (ví dụ: ebook, khóa học miễn phí,…).
Bước 4: Điền biểu mẫu
Người truy cập cung cấp thông tin cá nhân để đổi lấy đề nghị trên trang đích. Khi hoàn tất đăng ký, họ chính thức trở thành Lead của doanh nghiệp.
2. Marketing tạo Lead (Lead Generation Marketing)
Marketing để tạo khách hàng tiềm năng hay Lead Generation Marketing là việc sử dụng các kênh quảng cáo nhằm thu hút người lạ đến trang đích, chuyển đổi họ thành Lead và tiếp tục thúc đẩy họ trở thành khách hàng trả phí (Paid Customer). Quá trình này có thể được mô tả qua sơ đồ: Kênh quảng cáo → Trang đích → Lead → Khách hàng trả phí. Trên thực tế, doanh nghiệp thường kết hợp nhiều kênh khác nhau để tối ưu hiệu quả, tùy theo đặc điểm ngành hàng và đối tượng mục tiêu, nhằm đảm bảo dòng chảy khách hàng diễn ra liền mạch và hiệu quả hơn.
III. Làm thế nào để đánh giá Lead?
1. Đánh giá Lead dựa trên thông tin cung cấp
Người dùng thường sẵn sàng để lại thông tin cá nhân nếu họ nhận được một ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Tuy nhiên, mức độ quan tâm của mỗi người sẽ khác nhau tùy vào tình huống cụ thể.
Chẳng hạn, trong một chiến dịch marketing cho một dự án bất động sản:
Người dùng A chỉ đăng ký email để nhận bảng giá hoặc xem hình ảnh tổng quan dự án. Điều này cho thấy A mới chỉ quan tâm ở mức tham khảo. Người dùng B, ngoài việc đăng ký nhận thông tin, còn để lại số điện thoại, đặt lịch tư vấn, hoặc tham gia sự kiện mở bán. Điều này chứng tỏ B có nhu cầu mua cao hơn và đang trong giai đoạn cân nhắc nghiêm túc.
Dựa vào dữ liệu thu thập, doanh nghiệp có thể phân loại mức độ quan tâm của khách hàng và triển khai các chiến dịch remarketing hoặc tư vấn cá nhân hóa. Cách đánh giá này giúp doanh nghiệp lọc ra Lead chất lượng, tập trung nguồn lực vào những khách hàng có khả năng giao dịch cao nhất và tối ưu hiệu suất bán hàng.
2. Đánh giá Lead bằng Lead Scoring
Lead Scoring là phương pháp định lượng khách hàng tiềm năng bằng cách gán điểm số dựa trên hành vi và mức độ tương tác của họ. Mô hình này giúp doanh nghiệp xác định Lead đang ở giai đoạn nào trong hành trình từ quan tâm đến sẵn sàng mua hàng. Mỗi doanh nghiệp có bộ tiêu chí riêng để chấm điểm Lead, nhưng điều quan trọng là cần đảm bảo sự thống nhất giữa Marketing và Sales để tối ưu quy trình chuyển đổi và cải thiện hiệu quả bán hàng.
Ví dụ trong chiến dịch email marketing:
• Mở email: +1 điểm
• Nhấp vào liên kết trong email: +2 điểm
• Đăng ký nhận tư vấn hoặc tải tài liệu: +3 điểm
Nhờ vào hệ thống chấm điểm này, doanh nghiệp có thể dễ dàng phân loại Lead, từ đó tập trung vào những khách hàng tiềm năng có điểm số cao và đang gần gũi với quyết định mua hàng, giúp tối ưu hóa nguồn lực và tăng tỷ lệ chuyển đổi.
Dựa trên điểm số, doanh nghiệp có thể phân loại Lead thành lạnh – ấm – nóng và điều chỉnh chiến lược tiếp cận phù hợp. Việc tập trung vào đúng đối tượng, đúng nhu cầu sẽ giúp tăng tỷ lệ chuyển đổi và tối ưu hóa hiệu quả bán hàng.
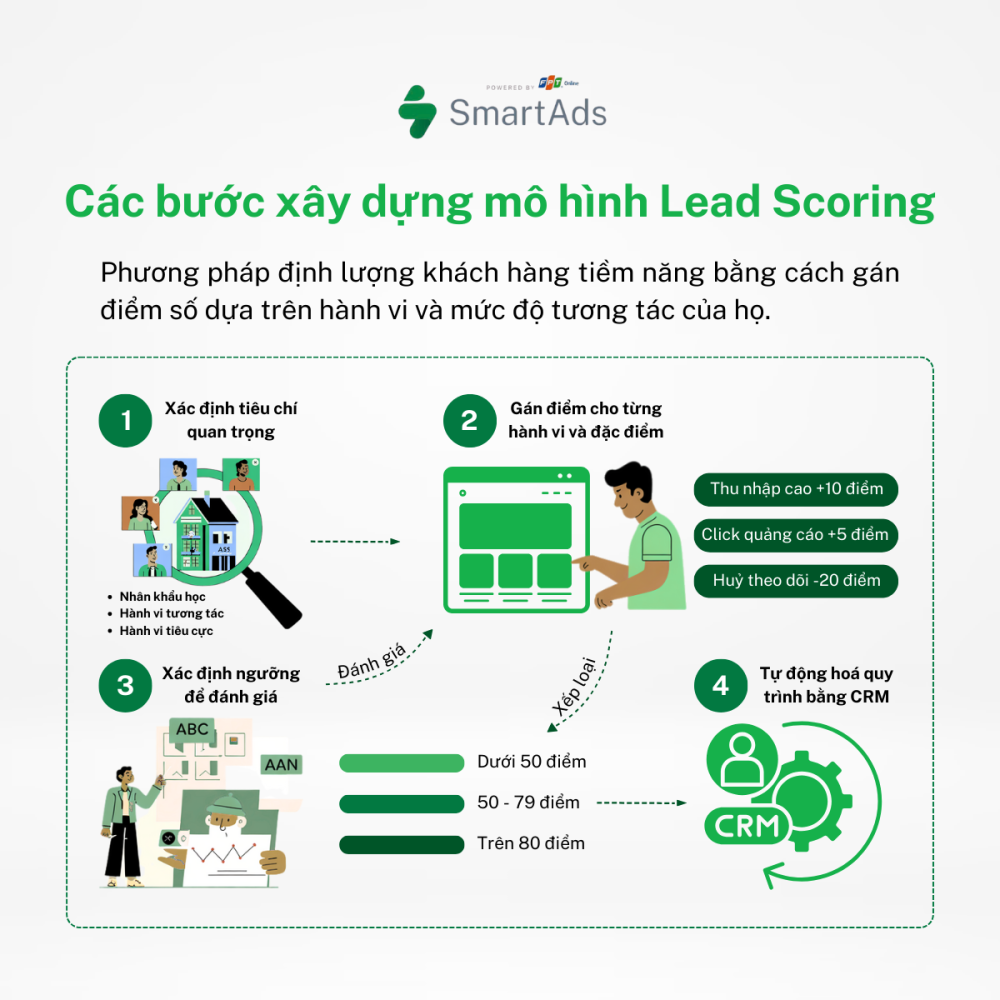
IV. Các bước xây dựng mô hình Lead Scoring
1. Xác định tiêu chí quan trọng
Bước đầu tiên là xác định các đặc điểm và hành vi thể hiện khả năng chuyển đổi của một Lead. Bao gồm:
• Yếu tố nhân khẩu học: Đặc điểm nào của khách hàng lý tưởng xuất hiện ở những Lead đã chuyển đổi trước đây?
• Yếu tố hành vi: Những tương tác nào với thương hiệu (ví dụ: mở email, truy cập website, dùng thử sản phẩm) có mối liên hệ với tỷ lệ chuyển đổi cao?
2. Gán điểm cho từng hành vi và đặc điểm
Sau khi xác định các hành vi và yếu tố quan trọng, hãy gán điểm số tương ứng theo mức độ ảnh hưởng của chúng.
3. Xác định ngưỡng để đánh giá Lead đủ điều kiện
Xác định số điểm tối thiểu mà một Lead cần đạt để được chuyển cho đội ngũ bán hàng. Ngưỡng này sẽ phụ thuộc vào quy trình của từng doanh nghiệp và có thể điều chỉnh theo thời gian để đảm bảo sự cân bằng giữa chất lượng và số lượng Lead.
4. Tự động hoá quy trình bằng CRM
Sử dụng các nền tảng CRM (Customer Relationship Management) giúp bạn tự động cập nhật điểm số Lead theo thời gian thực dựa trên hành vi tương tác của họ.
Case study: Anh X thấy quảng cáo dự án căn hộ ABC trên báo và click vào. Sau đó, anh truy cập website, xem bảng giá và đăng ký nhận tài liệu qua form. Hôm sau, anh chat với nhân viên để hỏi về phương thức thanh toán. Cuối cùng, anh đặt lịch hẹn xem nhà mẫu. Hành vi của anh X được tính điểm như sau:


Việc hiểu rõ Lead và xây dựng quy trình Lead Generation hiệu quả sẽ giúp doanh nghiệp tối ưu hóa chuyển đổi và tăng trưởng doanh thu. Bằng cách áp dụng mô hình Lead Scoring và các công cụ tự động hóa, doanh nghiệp có thể tập trung vào nhóm khách hàng tiềm năng chất lượng nhất, nâng cao hiệu suất của cả Marketing và Sales.
Hiện tại, SmartAds đang triển khai giải pháp Native Ads trên các trang báo điện tử giúp kết nối doanh nghiệp với 50 triệu độc giả tiềm năng thông qua mạng lưới Publisher Premium. Với 40.000 cơ hội tiếp cận các nhóm doanh nghiệp, SmartAds không chỉ là giải pháp giúp doanh nghiệp gia tăng độ nhận diện mà còn là giải pháp performance giúp doanh nghiệp cải thiện độ tin tưởng lên đến 27% và thu hút nhiều lead chất lượng.